bath and works, lewy body dementia, the body shop
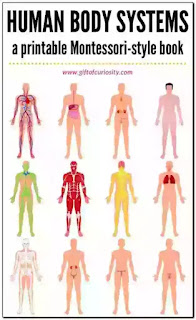
1All the body systems are dependent on one another, but have their own tasks.
2. The anchor for the muscles, which protects the major organs, is the skeleton
. 3. The one, which lets us move, are the skeletal muscles, muscles are also involved in other systems too.
4. Brain and the nerves compress the nervous system, which is the communication network and controls the body.
5. The digestive system breaks down food into chemicals that the body can use.
6. Without threatening life, only the reproductive system can be removed.
7. The organ, which lets people to have children, is the sexual organ: it is also the smallest of all the systems.
bath and works, lewy body dementia, the body shop
. 3. The one, which lets us move, are the skeletal muscles, muscles are also involved in other systems too.
4. Brain and the nerves compress the nervous system, which is the communication network and controls the body.
5. The digestive system breaks down food into chemicals that the body can use.
6. Without threatening life, only the reproductive system can be removed.
7. The organ, which lets people to have children, is the sexual organ: it is also the smallest of all the systems.
 |
| body system,bath and works, lewy body dementia, the body shop |
2. The Strell sign Le Beleen the bet and te bes is geleer spinta! dete
3. The stie ceud is endlesen tie neural SENE
4. At the age etter de sendicole stops growing
5. PELSCLE can be patel zec, the damages te situel Core
6. Spinal celt isetili len tiid but is 43 cm
7. 3 layers called es mening es cover spinal cord.
8. In spintel core, the central aree is made us of gray matter wlifelv is buiten slaped, while the outer alea is made of white matter
9. Tells (anons) of eve cells ferits wilte unetter; while gray matter is fomed by cell bedies eine ve vells
3. The stie ceud is endlesen tie neural SENE
4. At the age etter de sendicole stops growing
5. PELSCLE can be patel zec, the damages te situel Core
6. Spinal celt isetili len tiid but is 43 cm
7. 3 layers called es mening es cover spinal cord.
8. In spintel core, the central aree is made us of gray matter wlifelv is buiten slaped, while the outer alea is made of white matter
9. Tells (anons) of eve cells ferits wilte unetter; while gray matter is fomed by cell bedies eine ve vells
gene
Genes The fundamental physical unit of heredity is called gene. Inside every cell of our body there are more than 30,000 individual genes. Digesting fat from food, eye color, etc are controlled by small group of genes. A baby has half gene from mother while the other half from father. Only identical twins will have the same gene construction. No brothers or sisters have the same gene construction. DNA is shaped in a double helix, with linking bars. Thymine, cytosine, adenine, glucose are four chemicals of bars of DNA. DNA replication helps in the transfer of genetic information from one cell to another.
The Eye
1. Hard balls filled with jelly like substance called vitreous humor are our eyes.
2. A thin, glassy dish across our eye is the cornea, it makes light rays come through the eyes window, the pupil and then to the lens of the eyes.
3. The colored muscular ring around the pupil is the iris. In dim light iris widens whereas in bright light it narrows.
4. Optic nerve carries signal from eye to the brain.
5. Cones and rods are the two kinds of light-sensitive cells in the retina.
6. Cones detect colors, whereas rods cannot detect colors, but can work in even dim light.
7. Usually the dominant eye of both is the right one.
1. Hard balls filled with jelly like substance called vitreous humor are our eyes.
2. A thin, glassy dish across our eye is the cornea, it makes light rays come through the eyes window, the pupil and then to the lens of the eyes.
3. The colored muscular ring around the pupil is the iris. In dim light iris widens whereas in bright light it narrows.
4. Optic nerve carries signal from eye to the brain.
5. Cones and rods are the two kinds of light-sensitive cells in the retina.
6. Cones detect colors, whereas rods cannot detect colors, but can work in even dim light.
7. Usually the dominant eye of both is the right one.
5
The kidneys
1. Kidneys are purplish brown and bean shaped.
2. It is about 10 cm in length and 5 cm in breadth
3. Kidney cleans blood and also manages water in body.
4. Every minute about 1.3 liters of blood is filtered.
5. About 150 times blood is filtered as every ten minutes all the blood flows through kidney.
6. Only 0.6 liters is given as urine, whereas 85 liters of water and other substances from every 1000 liters of blood.
7. The kidneys save amino acids, glucose and about 70% of salt.
8. Each kidney bears a longitudinal opening on its concave side called hilum.
9. Each kidney consists of a vast number of microscopic tubular.
10. Nephrons are the structural and functional units of kidney.
1. Kidneys are purplish brown and bean shaped.
2. It is about 10 cm in length and 5 cm in breadth
3. Kidney cleans blood and also manages water in body.
4. Every minute about 1.3 liters of blood is filtered.
5. About 150 times blood is filtered as every ten minutes all the blood flows through kidney.
6. Only 0.6 liters is given as urine, whereas 85 liters of water and other substances from every 1000 liters of blood.
7. The kidneys save amino acids, glucose and about 70% of salt.
8. Each kidney bears a longitudinal opening on its concave side called hilum.
9. Each kidney consists of a vast number of microscopic tubular.
10. Nephrons are the structural and functional units of kidney.
Brain
1. About 100 million nerve cells, called neurons constituents a human brain.
2. There are trillions and trillions of different pathways for brain.
3. A boy's brain weighs about 2% of the body weight.
4. A girl's brain weighs about 2.5% of the body weight.
5. Every minute about 0.85 liters of blood is required by brain.
6. 15% of the entire blood in the body is required by brain.
7. Left part of our body is controlled by the right side of the brain, while the left part of brain controls the right part of body.
8. The cerebellum controls body co-ordination and balance.
9. In a laboratory dish, scientists can now grow brain cells.
1. About 100 million nerve cells, called neurons constituents a human brain.
2. There are trillions and trillions of different pathways for brain.
3. A boy's brain weighs about 2% of the body weight.
4. A girl's brain weighs about 2.5% of the body weight.
5. Every minute about 0.85 liters of blood is required by brain.
6. 15% of the entire blood in the body is required by brain.
7. Left part of our body is controlled by the right side of the brain, while the left part of brain controls the right part of body.
8. The cerebellum controls body co-ordination and balance.
9. In a laboratory dish, scientists can now grow brain cells.
Circulation
1. The process of carrying blood to every part of the body from heart and vice versa is called as circulation.
2. In 1628, English physician William Harvey discovered blood circulation.
3. Arteries and arterioles are the vessels through which blood is pumped from the heart.
4. Venules and veins are the vessels through which blood is sent back to heart.
5. Capillaries are the smallest tubes through which blood flows from arterioles to the venules.
6. Pulmonary and systemic are the two parts of blood circulation.
7. The blood short of oxygen is carried by pulmonary circulation.
8. The oxygen rich blood is carried by systemic circulation.
9. Brain is the part where most part of blood is required.
1. The process of carrying blood to every part of the body from heart and vice versa is called as circulation.
2. In 1628, English physician William Harvey discovered blood circulation.
3. Arteries and arterioles are the vessels through which blood is pumped from the heart.
4. Venules and veins are the vessels through which blood is sent back to heart.
5. Capillaries are the smallest tubes through which blood flows from arterioles to the venules.
6. Pulmonary and systemic are the two parts of blood circulation.
7. The blood short of oxygen is carried by pulmonary circulation.
8. The oxygen rich blood is carried by systemic circulation.
9. Brain is the part where most part of blood is required.
1. Small microscopic organisms that harm us by entering our body or some other way are called as germs.
2. "Pathogens' is the scientific word for 'genes'.
3. We would be suffering from some infectious disease if the germs in our body multiply.
4. Systemic infection is an infection that spreads through our body
5. Localized infection is an Infection that affects only a small part of our body.
6. Single-celled organisms, which are found everywhere, are the bacteria.
7. Multiplication of bacteria is very fast.
8. Tetanus and typhoid are some of the diseases that are caused by cocci, spirilla and bacilli, which are round cells, coils shaped and rod shaped respectively.
9. By taking over other cells, viruses live, as they cannot survive on their own.
10. HIV is the virus, which causes AIDS ( Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). By entering our body it weakens the body's system, which fights infections.
2. "Pathogens' is the scientific word for 'genes'.
3. We would be suffering from some infectious disease if the germs in our body multiply.
4. Systemic infection is an infection that spreads through our body
5. Localized infection is an Infection that affects only a small part of our body.
6. Single-celled organisms, which are found everywhere, are the bacteria.
7. Multiplication of bacteria is very fast.
8. Tetanus and typhoid are some of the diseases that are caused by cocci, spirilla and bacilli, which are round cells, coils shaped and rod shaped respectively.
9. By taking over other cells, viruses live, as they cannot survive on their own.
10. HIV is the virus, which causes AIDS ( Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). By entering our body it weakens the body's system, which fights infections.
0 1. The human heart is a red colored organ, about the size of a closed fist.
2. In an adult male it weighs about 300 grams, where as 250 grams in an adult female.
3. Pericardium is the double-walled membrane, which covers heart.
4. Pericardial fluid fills the space between the heart and its membrane.
5. Septum is the muscle wall, which divides the heart into two sides.
6. Blood is pumped only to lungs by the right side of heart, which is weaker and smaller
7. The left side of heart pumps blood all around the body, it is strong as compared to the right side. 8. Heart is divided into 4 compartments.
9. With every beat 70 ml of blood is pumped.
10. About 200 million liters of blood is pumped during an average lifetime. Bone
2. In an adult male it weighs about 300 grams, where as 250 grams in an adult female.
3. Pericardium is the double-walled membrane, which covers heart.
4. Pericardial fluid fills the space between the heart and its membrane.
5. Septum is the muscle wall, which divides the heart into two sides.
6. Blood is pumped only to lungs by the right side of heart, which is weaker and smaller
7. The left side of heart pumps blood all around the body, it is strong as compared to the right side. 8. Heart is divided into 4 compartments.
9. With every beat 70 ml of blood is pumped.
10. About 200 million liters of blood is pumped during an average lifetime. Bone
Bone
1. Bones contribute only 14% to the body weight.
2 Minerals like calcium and phosphate provide bones with inflexibility
3. While elastic fibers proves them with flexibility
, 4. Osteons reinforces the outside of bones.
5. Epiphyseal plate is the region where bones grow longer.
6. Metacarpals are the bones of the palm, where as carpals are the bones of the wrist.
7. There are 14 bones, which form the skeleton of face.
8. The vertebral column consists of 33 bones called vertebrae.
9. Phalanges are the bones of toes; there are fourteen phalanges in man.
10. Bones give the definite shape to the body
1. Bones contribute only 14% to the body weight.
2 Minerals like calcium and phosphate provide bones with inflexibility
3. While elastic fibers proves them with flexibility
, 4. Osteons reinforces the outside of bones.
5. Epiphyseal plate is the region where bones grow longer.
6. Metacarpals are the bones of the palm, where as carpals are the bones of the wrist.
7. There are 14 bones, which form the skeleton of face.
8. The vertebral column consists of 33 bones called vertebrae.
9. Phalanges are the bones of toes; there are fourteen phalanges in man.
10. Bones give the definite shape to the body
35
1. The place where a woman's body stores, releases and nurtures the egg cells is the reproductive system of a woman.
2. When a woman has sexual intercourse man's sperm enters the womb and fertilize the egg in the Fallopian tube.
3. Menstrual period is when the egg is not fertilized and it sheds with the womb lining in a flow of blood from the vagina.
4. When follicle - stimulating hormone (FSH) is released by pituitary gland then a monthly menstrual cycle begins.
5. Sex hormone estrogen is released as the follicle grows.
6. The lining of womb is thickened by estrogen.
7. Through Fallopian tube, the ripen egg slides down.
8. Follicle is a tiny sac where each egg is stored.
9. Through ovaries only a single egg cell is released during monthly menstrual cycle.
1. The place where a woman's body stores, releases and nurtures the egg cells is the reproductive system of a woman.
2. When a woman has sexual intercourse man's sperm enters the womb and fertilize the egg in the Fallopian tube.
3. Menstrual period is when the egg is not fertilized and it sheds with the womb lining in a flow of blood from the vagina.
4. When follicle - stimulating hormone (FSH) is released by pituitary gland then a monthly menstrual cycle begins.
5. Sex hormone estrogen is released as the follicle grows.
6. The lining of womb is thickened by estrogen.
7. Through Fallopian tube, the ripen egg slides down.
8. Follicle is a tiny sac where each egg is stored.
9. Through ovaries only a single egg cell is released during monthly menstrual cycle.
Reproduction boys
1. The place where body creates sperm cell is the reproductive system of man.
2. The one that appears like the microscopically tiny tadpoles are the sperm cells; it is produced in the scrotum, which is inside the testes.
3. To improve sperm production testes and scrotum are cooler as compared to the body temperature and they hang outside the body.
4. At 15, about 200 million sperms are produced a day.
5. A 6m long coiled tube epididmys leaves the sperms from testes.
6. During sexual intercourse sperm are driven into a tube called vas deferens
7. In testes the male sex hormone is produced.
2. The one that appears like the microscopically tiny tadpoles are the sperm cells; it is produced in the scrotum, which is inside the testes.
3. To improve sperm production testes and scrotum are cooler as compared to the body temperature and they hang outside the body.
4. At 15, about 200 million sperms are produced a day.
5. A 6m long coiled tube epididmys leaves the sperms from testes.
6. During sexual intercourse sperm are driven into a tube called vas deferens
7. In testes the male sex hormone is produced.
Squeezing of heart muscle to pump blood all over the body causes heartbeat. To make blood move only in one direction heart has four valves. Blood pressure is measured at two levels viz. systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. The maximum pressure exerts on the wall of arteries is called as systolic pressure 120 mm Hg is the normal adult man systolic pressure. The minimum pressure exerted on the walls of arteries is called as diastolic pressure. 80 mm Hg is the normal adult man diastolic pressure. The signals that make the heart beat faster or slower are the nerve signals. As the muscles of the heart are elastic, they easily contract and relax.
1. The transmission of genetic characters from one generation to another generation is called as heredity.
2. Genes pass characteristics.
3. About 150 years ago, Austrian monk Gregor Mendel discovered laws of heredity.
4. Law of dominance, law of segregation and law of independent assortment were the three laws discovered by Mendel.
5. The gene, which is unable to express itself, is called as recessive gene.
6. The gene, which expresses itself, is called as dominant gene.
7. Genotype is the genetic composition of an organism.
8. Phenotype is the physical appearance of an organism.
9. When the dominant character is not able to suppress the recessive character it is called as co - dominance.
2. Genes pass characteristics.
3. About 150 years ago, Austrian monk Gregor Mendel discovered laws of heredity.
4. Law of dominance, law of segregation and law of independent assortment were the three laws discovered by Mendel.
5. The gene, which is unable to express itself, is called as recessive gene.
6. The gene, which expresses itself, is called as dominant gene.
7. Genotype is the genetic composition of an organism.
8. Phenotype is the physical appearance of an organism.
9. When the dominant character is not able to suppress the recessive character it is called as co - dominance.
Skin
1 The protective coat, which shields us from the weather and maintains the appropriate temperature, is the skin.
2 Skin responds to heat, cold, touch and pressure, it is the largest receptor.
3. Using sunlight skin produces Vitamin D. The layer below epidermis is the dermis, which has sweat gland, also living cells.
bath and works, lewy body dementia, the body shop
1 The protective coat, which shields us from the weather and maintains the appropriate temperature, is the skin.
2 Skin responds to heat, cold, touch and pressure, it is the largest receptor.
3. Using sunlight skin produces Vitamin D. The layer below epidermis is the dermis, which has sweat gland, also living cells.
bath and works, lewy body dementia, the body shop